17 Oktober 2023 - 11:47

The Euler-Liljestrand mechanism regulates the perfusion of nonventilated alveoli: if a lung section is perfused but not ventilated, there will be a drop in the oxygen concentration in the blood, resulting in hypoxic vasoconstriction. The ventilation-perfusion ratio is higher in the apex of the lung than at its base.
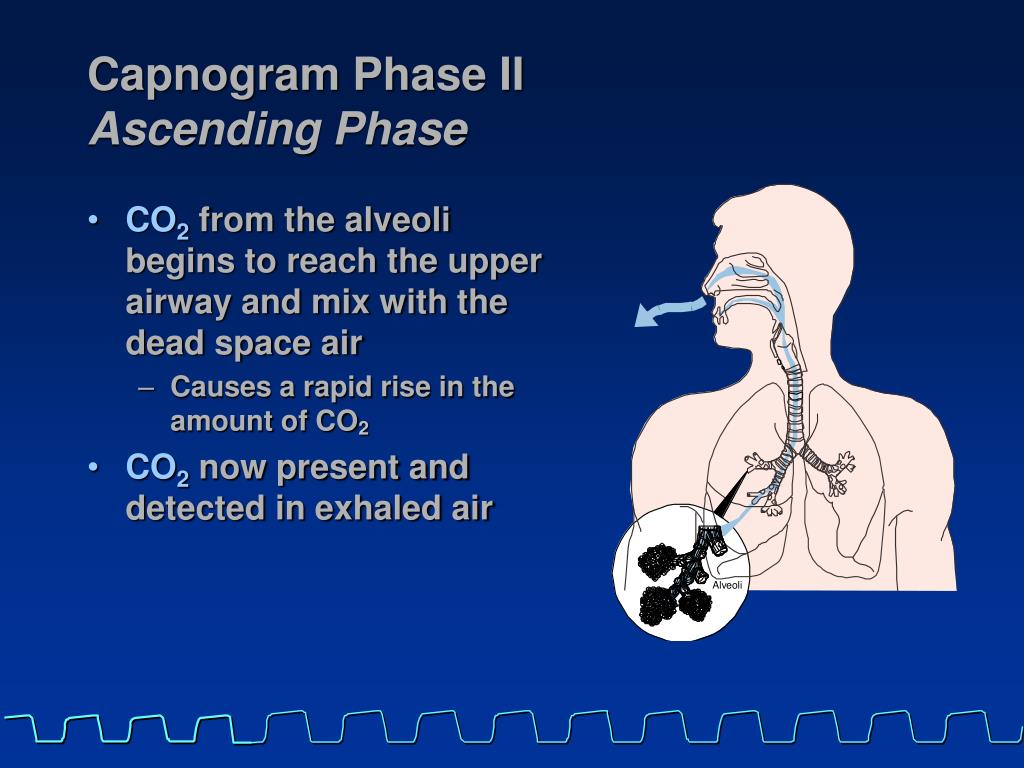
Perfusion of the pulmonary capillaries is closely regulated to match ventilation in order to maximize gas exchange. The physiologic dead space is the volume of inspired air that does not participate in gas exchange.

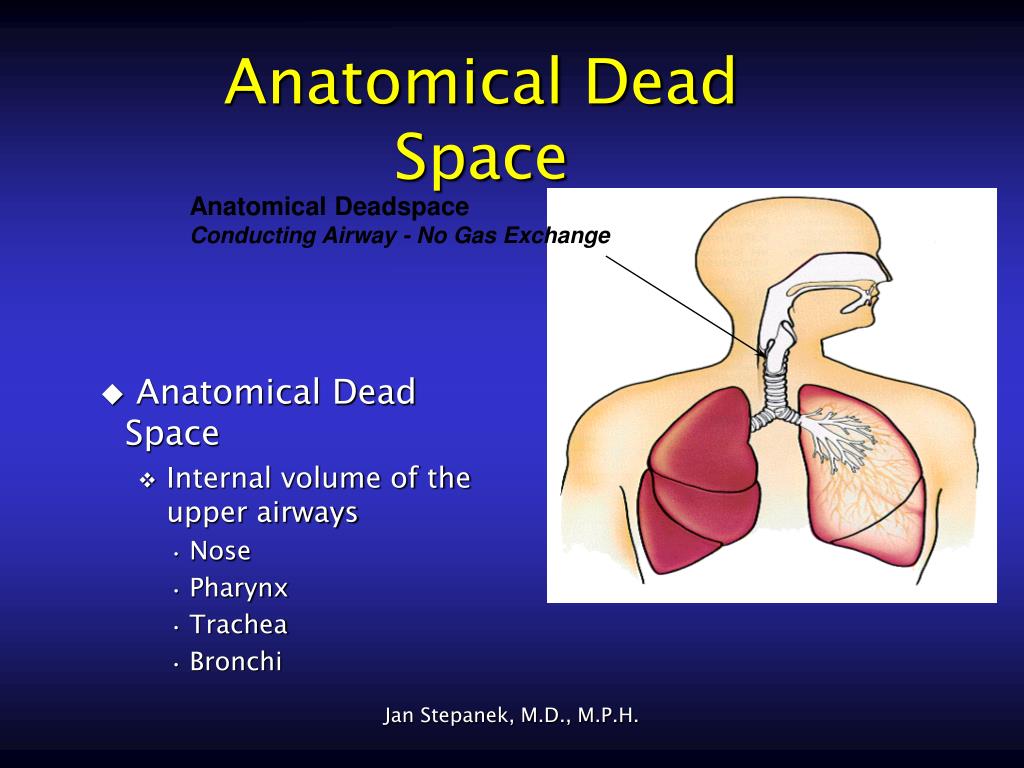
Ventilation is the movement of air through the respiratory tract into (inspiration) and out of (expiration) the respiratory zone ( lungs). The main function of the respiratory system is gas exchange (O 2 and CO 2).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
